GARP FRM Course Details 2025 Session
Offered by GARP (Global Association of Risk Professionals)
Looking for Classes, Books, Question Bank?
Notice
As per recent changes by GARP: FRM® Part I and Part II both exams will be held in May, August and Nov Exam windows in 2025.
About
Financial Risk
Manager (FRM®)
FRM, or Financial Risk Manager, is a professional certification offered by the Global Association of Risk Professionals (GARP). The FRM course is designed to provide individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to understand and manage financial risks in a variety of settings, including banks, insurance companies, and investment firms. The course covers a wide range of topics, including financial markets, statistical modeling, financial instruments, and risk management techniques. To earn the FRM certification, individuals must pass a rigorous two-part exam that tests their knowledge and understanding of these topics. The FRM course is highly regarded in the financial industry, and many employers seek out individuals who have earned the FRM certification.
FRM® exam pattern
The FRM exam is a two-part exam, with part I consisting of 100 MCQ and part II consisting of 80 MCQ. Part 1 of the exam covers the foundations of risk management, while Part 2 focuses on applications and models. The exam is administered on a computer and is offered on specific dates in the month of May, August and November in 2024.
| Exam Mode | Computer Based Testing |
| Total Questions | 100 MCQ (with 4 options) |
| Time Duration | 4 Hours |
| Total Subjects | 4 Subjects |
| Exam Mode | Computer Based Testing |
| Total Questions | 80 MCQ (with 4 Options) |
| Time Duration | 4 Hours |
| Total Subjects | 6 Subjects |
For FRM Part I and Part II Exam fees please check

Eligibility for Pursuing FRM®
Anyone can register to take the exam. There are no qualification requirements for FRM. However, from job perspective it is recommended to also own University Graduation or certifications like CA (chartered accountant), CS, or Actuaries (pursuing or completed). FRM certification is awarded after a candidate has passed two rigorous multiple choice exams (FRM Exam Part I and Part II) and demonstrated two years of relevant work experience.
Steps to become certified FRM®
-
Clear FRM Part I
4 Hour exam with 100 MCQ Questions
-
Clear FRM Part II
4 Hour exam with 80 MCQ Questions
-
Submit 2 Years of Work Experience
10 years prior to passing FRM Part II or within 5 years of Passing FRM Part II

Prepare FRM with Falcon Edufin
FRM® Study Package Highlights
We make your FRM journey smoother with our student friendly study content
Video Lessons
Over 120 hours of exam-oriented videos will help you better prepare within a shorter timeframe.
Question Bank
Question bank with more than 1500+ exam level question and concept builders.
FastTrack Videos
Cover all important topics in 35 hours with Fastrack videos. Best for revision and crash preparation.
Mock Test
10 Rounds of section wise test. 2 Rounds of Full Exam Level Mock Test.
Doubt Solving
One to one doubt solving by expert faculties via screen sharing or phone.
Study Notes
Easy To Understand Language, Information in the form of charts and tables. Key points pre highlighted.
For Exam window please check https://www.garp.org/frm/fees-payments
Subjects and Syllabus
FRM Part I

FRM Part II
FRM Foundations of Risk Management
This area focuses on a candidate’s knowledge of foundational concepts of risk management and how risk management can add value to an organization and includes:
- Basic risk types, measurement, and management tools
- Creating value with risk management
- Risk governance and corporate governance
- Credit risk transfer mechanisms
- The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
- Risk-adjusted performance measurement
- Multifactor models
- Data aggregation and risk reporting
- Financial disasters and risk management failures
- Ethics and the GARP Code of Conduct
- Enterprise risk management (ERM)
Quantitative Analysis
This area tests a candidate’s knowledge of basic probability and statistics; regression and time series analysis; and various quantitative techniques useful in risk management such as:
- Discrete and continuous probability distributions
- Estimating the parameters of distributions
- Population and sample statistics
- Bayesian analysis
- Statistical inference and hypothesis testing
- Measures of correlation
- Line regression with single and multiple regressors
- Time series analysis and forecasting
- Simulation methods
Financial Markets and Products
This area tests the candidate’s knowledge of financial products and the markets
in which they trade including:
- Structures and functions of financial institutions
- Structure and mechanics of over-the-counter (OTC) and exchange markets
- Structure, mechanics, and valuation of forwards, futures, swaps, and options
- Hedging with derivatives
- Interest rates and measures of interest rate sensitivity
- Foreign exchange risk
- Corporate bonds
- Mortgage-backed securities
Valuation and Risk Models | 30%
This area will test a candidate’s knowledge of valuation techniques and risk models such as:
- Value-at-Risk (VaR)
- Expected shortfall (ES)
- Estimating volatility and correlation
- Economic and regulatory capital
- Stress testing and scenario analysis
- Option valuation
- Fixed income valuation
- Hedging
- Country and sovereign risk models and management
- External and internal credit ratings
- Expected and unexpected losses
- Operational risk
Market Risk Measurement and Management
This area tests a candidate’s knowledge of market risk measurement and
management techniques. These include:
- VaR and other risk measures
- Parametric and non-parametric methods of estimation
- VaR mapping
- Back testing VaR
- Expected shortfall and other coherent risk measures
- Extreme Value Theory (EVT)
- Modeling dependence: correlations and copulas
- Term structure models of interest rates
- Volatility: Smiles and term structures
- Fundamental Review of the Trading Book
Credit Risk Measurement and Management
This area focuses on a candidate’s understanding of credit risk management with
some focus given to structured finance and credit products such as collateralized
debt obligations and credit derivatives. Areas of knowledge include:
- Credit analysis
- Default risk: Quantitative methodologies
- Expected and unexpected loss
- Credit VaR
- Counterparty risk
- Credit derivatives
- Structured finance and securitization
Operational Risk and Resiliency
This area addresses a candidate’s knowledge of two areas of increasing
importance for many firms — operational risk management and operational
resilience in the face of changing market conditions. This includes:
- Principles for sound operational risk management
- Risk appetite frameworks and enterprise risk management
- Risk culture and conduct
- Analyzing and reporting operational loss data
- Model risk and model validation
- Risk-adjusted return on capital (RAROC)
- Economic capital frameworks and capital planning
- Stress testing banks
- Third-party outsourcing risk
- Risks related to money laundering and financing of terrorism
- Regulation and the Basel Accords
- Cyber risk and cyber resilience
- Operational resilience
Liquidity and Treasury Risk Measurement and Management
This area tests a candidate’s understanding of liquidity and treasury risk
measurement and management techniques. These include:
- Liquidity risk principles and metrics
- Liquidity portfolio management
- Cash-flow modeling, liquidity stress testing, and reporting
- Contingency funding plan
- Funding models
- Funds transfer pricing
- Cross-currency funding
- Balance sheet management
- Asset liquidity
Risk Management and Investment Management
This area focuses on a candidate’s knowledge of risk management techniques
applied to the investment management process, including:
- Factor theory
- Portfolio construction
- Portfolio risk measures
- Risk budgeting
- Risk monitoring and performance measurement
- Portfolio-based performance analysis
- Hedge funds
Current issues in financial markets
This area tests a candidate’s knowledge of current issues in financial
markets, including:
- Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and “big data”
- Risk management implications of COVID-19
- Phasing out of LIBOR/Reference rates
- Climate risk
- Cyber resiliency in the wider financial system
- Digital currencies
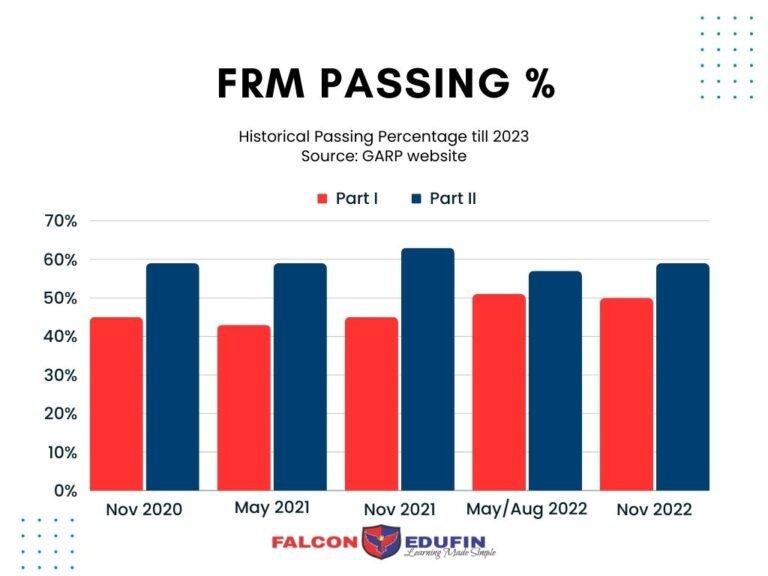
Pass Percentage from Recent Exam