- +91 9096131868
- falconedufin@gmail.com
- All Day: 10:30 AM - 9:30 PM IST
How can we help you?
C17 CENTRAL CLEARING
Reading Time: 4 min read
THE ROLE OF A CENTRAL COUNTERPARTY #
- CLEARING & SETTLEMENT : Clearing refers to the process (including margining & netting) between the period from trade execution until settlement. Settlement of a trade occurs when the trade is completed and all payments have been made and legal obligations satisfied. A CCPs primary function is to simplify the operational process and reduce counterparty risk that exists ina the bilateral market.
- AUCTIONS & LOSS MUTUALIZATION: Key functions of a CCP related to the clearing process include: margining, novation, netting, managing the auction process and loss mutualisation. When a Central clearing member defaults, rather than closing out the trades at market value, the CCP typically auctions off the trades to the surviving members through an auctioning process. Loss mutualisation is a form of insurance & refers to member’s contributions to a default fund to cover future losses from member defaults. So when a member does defaults, any amount that cannot be covered from the member’s own resources are covered from the fund.
OTHER MECHANICS OF A CCP #
PRODUCTS:
Currently there are four categories in OTC derivatives according to their stages of central clearing history:
- Products with long history of central clearing (int. rate swaps)
- Products with short history of central clearing (index CDS)
- Products that may soon be centrally cleared (CDS).
- Products that are not suitable for central clearing (exotic derivatives).
For a product to be centrally cleared, the contract should be standardized, need to be easily valued & should be liquid.
PARTCIPANTS:
Only clearing members can transact with CCP. Requirements for becoming a member includes:
- Admission criteria: CCPs set different admission criteria like credit quality & size.
- Financial commitments: Members should contribute to the CCP’s default fund.
- Operational Criteria: It includes posting margin, participating in “fire drills” to simulate member default & in auctions if default does occur.
NUMBER OF CCPs:
Although a single large CCP can benefit from economies of scale, it is not feasible to have a single CCP because:
- Regional difference : beneficial to centrally clear trades in the region’s currency & under the laws & regulations of the region.
- Product types: Often specialize in clearing certain derivatives products.
- Regulatory reasons: Regulations may dictate that products be cleared by local CCPs.
TYPES OF CCPs
Utility Driven Profit Driven

FAILURE OF A CCP #
CCPs have systemic risk & its failure can lead to catastrophic events. Therefore, it must maintain sufficient loss absorption methods to withhold large member defaults.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OTC DERIVATIVES & CCP/EXCHANGE #
| OTC DERIVATIVES | CCP/EXCHANGE | |
| Trading | Bilateral | Bilateral/Centralized |
| Counterparty | Original trade CP | CCP |
| Participants | All | Clearing Members |
| Products | All | Standard, Vanilla |
| Margining | Bilateral, custom | Full margining set by CCP |
| Loss buffers | Margin, regulatory capital | Initial margin, default fund, CCP capital |
ADVANTAGES OF CENTRAL CLEARING #
- TRANSPARENCY: CCPs have a consolidated view of trading positions and can therefore better react to extreme events.
- OFFSETTING: Duplicate bilateral contracts can be offset improving flexibility & reducing cost.
- LOSS MUTUALIZATION: A member losses are distributed among all surviving members minimizing market impact & systemic risk.
- LEGAL & OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY: The centralized role in clearing & settlement improves operational efficiency.
- LIQUIDITY: Daily margining of products ensures transparency in product valuation which increases product liquidity.
- DEFAULT MANAGEMENT: It acts counterparty to each trade reducing counterparty risk.
DISADVANTAGES OF CENTRAL CLEARING #
- MORAL HAZARD: One party can take on higher risk knowing that other parties bears the costs of this risk.
- ADVERSE SELECTION : Risk that participants with a better understanding of product risk & pricing will trade more products whose risks the CCP underprices.
- BIFURCATION: The separation of trading into cleared and non-cleared products can increase cash flow volatility even for hedged products.
- PROCYCLICALITY: It reflects a scenario where a CCP increases margin requirements (initial margin) in volatile market or during a crises, which may aggravate systemic risk.
MARGINING #
Margining involves posting cash or marketable security collateral by the member.
- Initial Margin : Cash or liquid assets transferred by a member at trade inception.
- Variation Margin : Cash posted by a member to cover the daily net change of the member’s position.
NOVATION & NETTING #
The legal process of interposing the CCP between seller & the buyer is called Novation. Through novation, one contract is replaced with another contract with the CCP.
When trades are novated to a CCP, these redundant trades become a single net obligation between each participant & the CCP. This process is called multilateral offsetting or netting. Netting reduces total risk & minimizes the potential of a domino effect stemming from the default of a participant.

BILATERAL OTC MARKET

NOVATION TO CCP
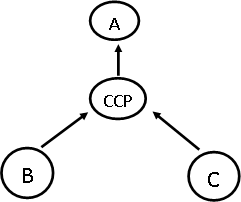
CCP NETTING
Updated on August 31, 2022





